A Comprehensive Guide to Paper Types & Printing Essentials
Paper is more than just a medium for writing and printing; it's a versatile and diverse material that serves a multitude of purposes. From the delicate tissue paper used to protect fragile items to the robust cardstock for wedding invitations, choosing the right type of paper can make all the difference in the outcome of your project.
Whether you're a casual user printing at home or a professional creating high-end promotional materials, understanding the various paper types and their ideal uses is crucial. In this guide, we'll explore different types of paper for printing, their weights, and finishes, as well as considerations for customised artwork and printing. Let's dive into the fascinating world of paper!
What is GSM?

GSM stands for "Grams per Square Meter" and is a unit of measurement used to indicate the weight or thickness of paper or other materials. It measures the mass of a square meter of the material, indicating its density or thickness. In the context of paper, higher GSM values generally indicate thicker and more durable paper, while lower GSM values indicate thinner and lighter paper.
Seven most used GSM classifications for paper

1. 35 – 55 gsm Paper
This lightweight paper, ideal for delicate tasks like tracing or protecting items, offers unparalleled delicacy and transparency. Often found in tissue and tracing paper, It provides a feather-light touch for intricate designs and sensitive projects.
2. 70 – 90 gsm Paper
Versatile and commonly used in printing and copying, this light to medium-weight paper guarantees crisp, clear reproduction of text and images. Perfect for everyday office tasks and stationery needs, it strikes a balance between affordability and quality.
3. 90 – 120 gsm Paper
Offering a step up in durability and substance, this medium-weight paper is favoured for promotional materials like flyers and brochures. Its sturdiness ensures longevity while still maintaining flexibility for easy handling and distribution.
4. 120 – 160 gsm Paper
With increased thickness and rigidity, this medium to heavy-weight paper is the choice for projects requiring a touch of sophistication. Perfect for high-quality printing such as visiting cards and invitations, it exudes elegance and professionalism in every detail.
5. 180 – 220 gsm Paper
Exuding a luxurious feel and impressive heft, this heavyweight paper is reserved for premium printing projects. Whether it's showcasing precious memories in photo prints or making a statement with artistic creations, its substantial weight ensures a lasting impression.
6. 250 – 300 gsm Paper
Known for its durability and resilience, this hefty paper is the go-to for projects requiring exceptional strength. From business cards to packaging materials, its robustness ensures that every piece stands out with solidity and reliability.
7. 300+ gsm Paper
Reserved for the most demanding printing tasks, this weighty paper sets the standard for excellence. Its substantial weight and thickness make it the top choice for projects where quality and durability are non-negotiable, ensuring a lasting impact that commands attention.
Now let's look into.
12 Different Types of Paper and Their Uses

1. Bond Paper

Bond paper is a durable, high-quality paper that is commonly used for writing, printing, and photocopying. It's known for its smooth texture and is often used for letterheads, office documents, legal forms, and stationery. Bond paper may also have watermarks for security purposes, as seen in official documents like certificates and legal papers.
2. Alabaster Paper

Alabaster paper is a type of high-quality, smooth paper with a subtle sheen. It's commonly used for art prints, fine stationery, invitations, and high-end brochures or catalogues. Alabaster paper's smooth surface and elegant appearance make it ideal for projects requiring a polished and professional look.
3. Kraft Paper
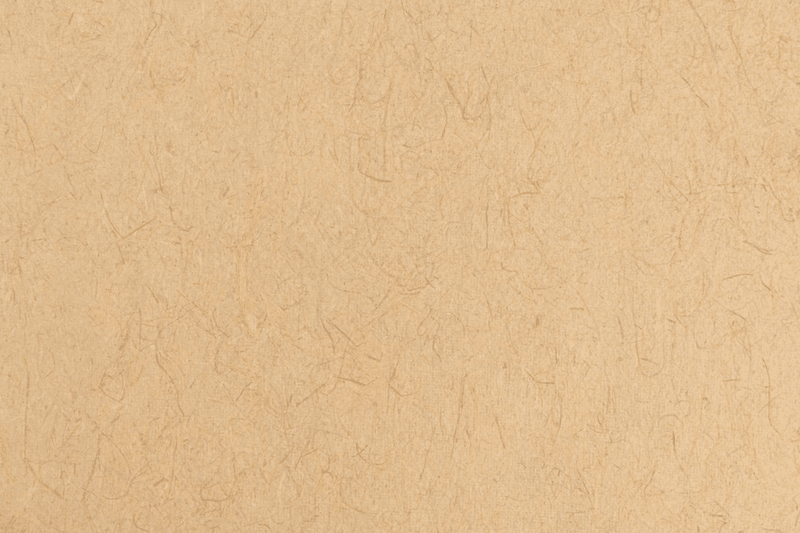

Kraft paper is a sturdy, brown paper made from recycled materials. It's known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for packaging, wrapping, and shipping parcels and packages. Kraft paper is also used for crafts, such as gift wrapping, book covers, carry bags and DIY projects, due to its natural appearance and eco-friendly properties.
4. Newsprint

Newsprint is a low-cost, lightweight paper with a slightly rough texture. It's primarily used for printing newspapers, flyers, and advertising inserts due to its affordability and ability to absorb ink quickly. Newsprint is also used for sketching, drawing, and packing fragile items.
5. Cardstock

Cardstock is a heavyweight paper often used for projects requiring extra durability and stiffness, such as greeting cards, invitations, business cards, and scrapbooking. It comes in various thicknesses and finishes, including matte, glossy, and textured, offering versatility for a wide range of creative projects.
6. Standard paper
Standard paper, ubiquitous in offices and homes, serves as the foundation for everyday printing tasks. Typically A4 in size, it offers a balance of affordability and quality, suitable for printing documents, reports, and letters. Its versatility and widespread availability make it an indispensable component of modern communication.
7. Glossy Paper
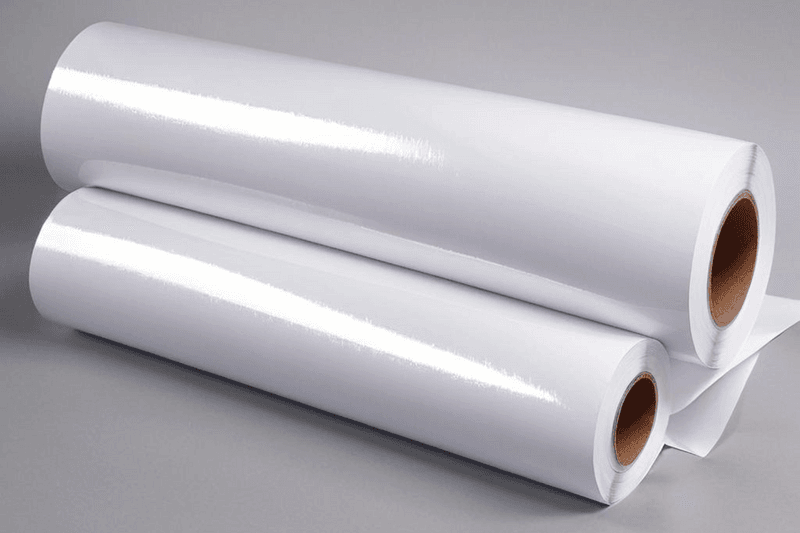

The glossy paper boasts a sleek surface that elevates printed images with vivid colours and sharp details, making it ideal for photographs and promotional materials. Its reflective finish adds a professional touch, catching the eye and enhancing visual appeal, whether for personal snapshots or professional presentations.
8. White Paper

White paper, the quintessential choice for printing, provides a pristine backdrop that ensures optimal contrast and readability for text and graphics. Its neutral hue lends versatility, suiting a myriad of applications from business reports to creative projects, where clarity and professionalism are paramount.
9. Photo Paper

Tailored for capturing moments in stunning detail, photo paper delivers prints with lifelike colour reproduction and crisp clarity. Available in various finishes like glossy or matte, it preserves memories with archival quality, ensuring photographs remain vivid and vibrant for generations to come, a timeless testament to cherished moments.
10. Textured Paper

Textured paper adds depth and character to printed materials with its tactile surface, ranging from subtly embossed to heavily textured designs. Ideal for invitations, artistic projects, and premium stationery, it imparts a sense of luxury and craftsmanship, inviting touch and engagement beyond the visual realm.
11. Non Tearable Paper

Non-tearable paper, engineered for durability and resilience, withstands rough handling and adverse conditions without tearing or damage. This is one of the commonly used paper types for outdoor signage, maps, and documents requiring longevity, it ensures information remains intact and legible, offering peace of mind in demanding environments.
12. Recycled Paper

Recycled paper, crafted from post-consumer waste or sustainable sources, reduces environmental impact while offering quality and functionality. Embraced for its eco-friendly credentials, it's suitable for a range of applications from office printing to packaging, contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
13. Metallic Paper

Metallic paper adds a touch of glamour and sophistication to printed materials with its shimmering finish and reflective properties. Popular for special occasions, invitations, and artistic projects, it infuses designs with a metallic sheen, catching the light and captivating attention for a dazzling impact.
Let’s move to the next section lamination!
Types of Lamination in Paper Printing

1. Glossy Lamination
Glossy lamination adds a shiny, reflective finish to printed materials, enhancing colours and providing a vibrant look. It's popular for marketing materials like brochures, posters, and magazine covers, as well as for packaging to give products a polished appearance.
2. Matte Lamination

Matte lamination creates a smooth, non-reflective finish with a subtle sheen. It reduces glare and fingerprints, giving printed materials a sophisticated and understated look. Matte lamination is commonly used for business cards, book covers, and luxury packaging.
3. Soft Touch Lamination
Soft touch lamination, also known as velvet or suede lamination, creates a luxurious, tactile finish that feels soft to the touch. It adds a velvety texture to printed materials, enhancing their appearance and perceived value. Soft touch lamination is often used for high-end packaging, presentation folders, and promotional materials.
4. Spot UV Lamination
Spot UV lamination involves applying a glossy, raised coating to specific areas of a printed piece, creating contrast and visual interest. It can be used to highlight logos, text, or images, adding a tactile and eye-catching element to the design. Spot UV lamination is popular for business cards, invitations, and marketing collateral.
5. Embossed Lamination

Embossed lamination adds texture and dimension to printed materials by pressing a raised pattern or design into the surface of the laminate. It creates a tactile and visually appealing effect, enhancing the overall look and feel of the printed piece. Embossed lamination is often used for book covers, packaging, and promotional materials.
If you are not yet ready to customise your project here are a few tips:
Things to keep in mind when giving customised artwork for printing.

1. File format and resolution
Provide artwork in a high-resolution format like TIFF or PDF to ensure clarity and sharpness in printing. Check that images are at least 300 dpi to prevent pixelation, guaranteeing crisp results that accurately represent your design vision.
2. Colour mode
Select the appropriate colour mode, usually CMYK for print, to ensure accurate colour reproduction. Avoid RGB, which is used for digital screens, to prevent colour discrepancies between screen and print. Consistent colour mode ensures your artwork looks as intended in the final printed product.
3. Bleed and trim marks
Extend your design beyond the final trim line to include bleed, typically 3mm, to prevent white edges. Include trim marks to guide precise cutting, ensuring your artwork fits seamlessly on the finished product without unwanted borders or gaps.
4. Font size and style
Choose legible fonts and appropriate sizes to ensure readability, especially for smaller text or intricate designs. Avoid overly complex or thin fonts that may not translate well in print, opting for clear, well-defined typography that enhances rather than detracts from your message.
5. Proofread and review
Thoroughly proofread your artwork for any spelling mistakes/grammatical errors, or design inconsistencies before sending it for printing. Take the time to review every detail, from text alignment to image placement, to ensure accuracy and professionalism in the final printed piece.
6. Material and finish
Consider the material and finish of the printed product to tailor your artwork accordingly. Account for factors like paper type, coating (e.g., matte or glossy), and special finishes (e.g., embossing or foil stamping) to enhance the visual impact and tactile experience of your design.
7. Communicate with the printer
Maintain open communication with your printer throughout the process, discussing specifications, deadlines, and any special requirements. Clarify expectations and address any concerns or questions to ensure a smooth printing process and satisfactory results that meet your vision and objectives.
Conclusion
The world of paper is rich and varied, offering multiple kinds of paper to suit every printing need and creative endeavour. Whether it's choosing the right GSM for durability or selecting the perfect lamination for a polished finish, attention to detail ensures that your printed materials make a lasting impression.
PrintStop has been providing customised products for the last 17 years, By understanding the nuances of paper types, finishes, and printing considerations, you can enhance your projects to new heights of quality and professionalism. So, explore, experiment, and embrace the diverse possibilities that paper has to offer, and let your imagination soar as you bring your visions to life on the printed page.